7 Natural Cures for Hemorrhoids - Get Relief in 24 Hours or Less
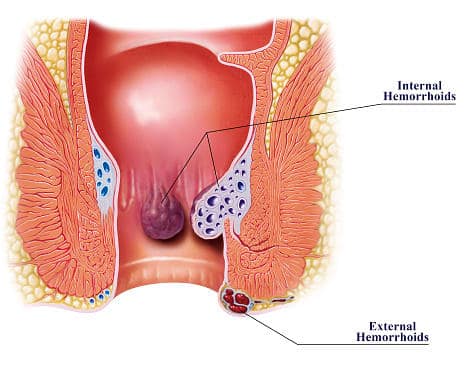
Internal hemorrhoids appear inside the lower rectum and are not visible to the naked eye. This type of hemorrhoid may not cause any pain or irritation, but a person may have other symptoms. Hemorrhoids are a common problem during pregnancy. The extra weight that a woman carries during pregnancy may place a strain on the veins in the anus and rectum. Hormonal and physical changes can also cause gastrointestinal problems, such as constipation or diarrhea, which increase a person's risk of hemorrhoids.
How long hemorrhoids last can vary from person to person, but a range of OTC remedies and medical options are available to treat them. There are also some simple changes that people can make to their diet and lifestyle to achieve symptom relief and prevent new hemorrhoids from forming.
Article last reviewed by Tue 4 September All references are available in the References tab. The evaluation and treatment of hemorrhoids: A guide for the gastroenterologist. From basic pathophysiology to clinical management. MNT is the registered trade mark of Healthline Media. Any medical information published on this website is not intended as a substitute for informed medical advice and you should not take any action before consulting with a healthcare professional.
Privacy Terms Ad policy Careers. This page was printed from: Get the most out of Medical News Today. Subscribe to our Newsletter to recieve: Professionally-verified articles Daily or weekly updates Content custom-tailored to your needs Create an account. More Sign up for our newsletter Discover in-depth, condition specific articles written by our in-house team.
Piles - FIVE cheap home treatments to get rid of your haemorrhoids
Please accept our privacy terms We use cookies and similar technologies to improve your browsing experience, personalize content and offers, show targeted ads, analyze traffic, and better understand you. Sign in Log in with your Medical News Today account to create or edit your custom homepage, catch-up on your opinions notifications and set your newsletter preferences. Register for a free account Sign up for a free Medical News Today account to customize your medical and health news experiences.
Register take the tour. A person with hemorrhoids may find sitting down very uncomfortable. Six home remedies for hemorrhoids. Hemorrhoids, also known as piles, often go away without treatment. However, a range of home remedies can help relieve uncomfortable symptoms. Eating plenty of fiber-rich foods may soften the stool, making it easier to pass. The extra weight that a woman carries during pregnancy may cause hemorrhoids. This content requires JavaScript to be enabled. Please use one of the following formats to cite this article in your essay, paper or report: If no author information is provided, the source is cited instead.
Latest news Simply receiving DNA test results can alter your physiology. A fascinating new study demonstrates that simply being told we have a genetic risk can alter the way our body behaves, even if the risk does not exist. Gut bacteria may influence drug effectiveness.
A new review of existing research examines the effect of the gut bacteria composition on the effectiveness of type 2 diabetes medications. Recalled 'weight history' can predict heart failure risk. While obesity can raise heart failure risk at any age, the risk is higher in those with a lifetime history of obesity compared with only recent obesity. Type 2 diabetes and cognitive decline: New research examines cognitive function and brain atrophy in both people with and without type 2 diabetes over the course of approximately 5 years.
Some types of food and lifestyle, including low fiber diet, spicy foods and alcohol intake, was reported to link with the development of hemorrhoids and the aggravation of acute hemorrhoid symptoms[ 15 ]. The most common presentation of hemorrhoids is painless rectal bleeding during defecation with or without prolapsing anal tissue.
- Treatment of hemorrhoids: A coloproctologist’s view.
- Wolf Bait: How to Seduce an Alpha (A BBW Paranormal Werewolf Shifter Erotic Romance).
- Success on the Tenure Track: Five Keys to Faculty Job Satisfaction.
- Latest Stories!
- 6 self-help tips for hemorrhoid flare-ups - Harvard Health Blog - Harvard Health Publishing;
- Othon (French Edition)?
The blood is normally not mixed in stool but instead coated on the outer surface of stool, or it is seen during cleansing after bowel movement. The blood is typically bright red since hemorrhoid plexus has direct arteriovenous communication[ 10 ]. Patients with complicated hemorrhoids such as acutely thrombosed external hemorrhoids and strangulated internal hemorrhoids may present with anal pain and lump at the anal verge.
It is uncommon that patients with uncomplicated hemorrhoid manifest any anal pain. In fact, severe anal pain in patient with hemorrhoids is more likely due to anal fissure and anorectal abscess[ 2 ].
Browse by Topic
A precise history and thorough physical examination, including digital rectal examination and anoscopy, are imperative for the diagnosis of hemorrhoids. Unless bright red blood is clearly seen from hemorrhoids, any patients with rectal bleeding should be scheduled for flexible sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy, especially those being at risk of colorectal cancer[ 1 , 2 ]. Hemorrhoids are generally classified by their location; internal originates above the dentate line and covered by anal mucosa , external originates below the dentate line and covered by anoderm and mixed type.
Internal hemorrhoids are further graded based on their appearance and degree of prolapse: An operation is usually indicated in low-graded hemorrhoids refractory to non-surgical treatment, high-graded hemorrhoids, and strangulated hemorrhoids[ 2 ]. Meanwhile, external hemorrhoid requires no specific treatment unless it becomes acutely thrombosed or causes patient discomfort. Current treatment of internal hemorrhoids based on their severity and degree of prolapse. Doppler-guided hemorrhoidal artery ligation; SH: Procedure for prolapse and hemorrhoids.
Although there is relatively little information of the efficacy of dietary and lifestyle modification on the treatment of hemorrhoids, many physicians include advice on dietary and lifestyle modification as a part of conservative treatment of hemorrhoids and as a preventive measure. The advice usually includes increasing the intake of dietary fiber and oral fluid, having regular exercise, refraining from straining and reading on the toilet, and avoiding drug causing constipation or diarrhea.
The main goal of medical treatment is to control acute symptoms of hemorrhoids rather than to cure the underlying hemorrhoids. There are several modern drugs and traditional medicine used which are available in a variety of format including pill, suppository, cream and wipes. However, the published literature lacks strong evidence supporting the true efficacy of topical treatment for symptomatic hemorrhoids. For an oral preparation, flavonoids are the most common phlebotonic agent used for treating hemorrhoids[ 18 ].
It is apparent that flavonoids could increase vascular tone, reduce venous capacity, decrease capillary permeability, facilitate lymphatic drainage and has anti-inflammatory effects[ 2 ]. A large meta-analysis of phlebotonics for hemorrhoids in showed that phlebotonics had significant beneficial effects on bleeding, pruritus, discharge and overall symptom improvement.
Piles - FIVE cheap home treatments to get rid of your haemorrhoids | www.newyorkethnicfood.com
Phlebotonics also alleviated post-hemorrhoidectomy symptoms[ 19 ]. Among several office-based procedures, rubber band ligation RBL appeared to have the lowest incidence of recurrent symptom and the need for retreatment[ 20 ]. RBL is also the most popular non-surgical intervention for hemorrhoids performed by surgeons[ 21 ]. It is a relatively safe and painless procedure with minimal complication. However, RBL is contraindicated in patient with anticoagulants or bleeding disorder, and those with concurrent anorectal sepsis.
With a technical note, the proper position of rubber band should be at the base of hemorrhoid bundle or over the bleeding site, but not too close to the dentate line. Vacuum suction ligator may offer clearer visualisation of hemorrhoids and more precise placement of banding when compared to a traditional forcep ligator[ 22 ].
Multiple sites and serial sessions of banding may be required for large internal hemorrhoids. Surgical intervention is usually required in low-graded hemorrhoids refractory to non-surgical treatment, high-graded symptomatic hemorrhoids, and hemorrhoids with complication such as strangulation and thrombosis. An ideal operation for hemorrhoids should remove internal and external component of hemorrhoids completely, have minimal postoperative pain and complication, demonstrate less recurrence, and are easy to learn and perform. The procedure could be cheap and cost-effective too. Unfortunately, none of the currently available operation achieves all the ideal conditions.
Piles treatment: How to get rid of symptoms (and prevent new haemorrhoids).
So far, excisional hemorrhoidectomy is the mainstay operation for grade III-IV hemorrhoids and complicated hemorrhoids. Of note, closed Ferguson hemorrhoidectomy and open Milligan-Morgan hemorrhoidectomy were equally effective and safe[ 23 , 24 ], but the Ferguson method was superior to the Milligan-Morgan method in term of long time patient satisfaction and continence[ 25 ]. Nevertheless, both techniques may lead to severe postoperative pain[ 26 ].
In order to minimize or avoid post-hemorrhoidectomy pain, more recent approaches including Ligasure hemorrhoidectomy, doppler-guided hemorrhoidal artery ligation and stapled hemorrhoidopexy have been adopted into the surgical treatment of hemorrhoids. In addition, perioperative care for hemorrhoids has been significantly improved[ 1 , 27 ]. A recent Cochrane Review demonstrates that Ligasure hemorrhoidectomy resulted in shorter operative time, less postoperative pain, and shorter convalescence period when compared to conventional hemorrhoidectomy[ 28 ].
Meanwhile, there was no significant difference in postoperative complications and long-term outcomes between the two techniques. Excisional hemorrhoidectomy can be performed safely in a day-case basis under the perianal infiltration of local anesthetics[ 29 ], or regional anesthesia, or general anesthesia. It is evident that some medications could decrease post-hemorrhoidectomy pain such as perioperative analgesia with oral non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs[ 30 ] and gabapentin[ 31 ], topical administration of sucralfate[ 32 ] or metronidazole[ 33 ], and postoperative administration of phlebotonic drugs[ 19 ].
Non-excisional operation for hemorrhoids includes doppler-guided hemorrhoidal artery ligation DG-HAL or known as transanal hemorrhoidal dearterialization THD , and plication of hemorrhoids or known as ligation anopexy or mucopexy. DG-HAL has been introduced into a surgical practice to cut off the blood supply to hemorrhoids without the need of hemorrhoid removal. It involves the surgical ligation of terminal branches of superior hemorrhoidal artery causing shrinkage of hemorrhoid bundles.
Meanwhile, a ligation anopexy or mucopexy was also demonstrated to be a good alternative to excisional hemorrhoidectomy for grade II-III hemorrhoids, with shorter operative time and lower postoperative pain[ 35 ]. Given the fact that there is the possibility of revascularization and recurrent prolapse, further studies on the long-term outcomes of non-excisional operations for hemorrhoids are needed. Stapled hemorrhoidopexy, also known as a procedure for prolapse and hemorrhoids PPH , is an alternative operation for treating advanced internal hemorrhoids.
A circular staple device is used to excise a ring of redundant rectal mucosa just above hemorrhoid bundles - not hemorrhoids per se. By doing this, prolapsing hemorrhoids will be repositioning hemorrhoidopexy and shrinking due to a partial interruption of blood supply to hemorrhoid plexus. Interestingly, the latest meta-analysis comparing surgical outcomes between stapled hemorrhoidopexy and Ligasure hemorrhoidectomy in revealed that both surgical techniques were practically comparable - with a slightly favorable immediate postoperative results and technical advantages for Ligasure hemorrhoidectomy[ 37 ].
Given the fact that stapled hemorrhoidopexy did not offer any significant advantages over Ligasure hemorrhoidectomy[ 37 ] and it is a relatively expensive operation which may cause serious postoperative complications such as rectal stricture and rectal perforation[ 38 ] as well as severe chronic anal pain[ 39 ], stapled hemorrhoidopexy should be reserved for patients with circumferential prolapsing hemorrhoids and it must be performed by a well-trained surgeon[ 2 ].
How long do hemorrhoids last? What to know
Patients with acutely thrombosed or strangulated internal hemorrhoids usually present with severely painful and irreducible hemorrhoids. The incarcerated hemorrhoids may become necrotic and drain. Manual reduction of the hemorrhoid masses, with or without intravenous analgesia or sedation, might help reducing pain and tissue congestion. Urgent hemorrhoidectomy is usually required in these circumstances.
Unless the tissues are necrotic, mucosa and anoderm should be preserved as much as possible to prevent postoperative anal stricture. In expert hands, surgical outcomes of urgent hemorrhoidectomy were comparable to those of elective hemorrhoidectomy[ 40 ]. Strangulated internal hemorrhoid; B: Acutely thrombosed external hemorrhoid.
Acutely thrombosed external hemorrhoids often develop in patients with acute constipation, or those with a recent history of prolonged straining. The severity of pain is most intense within the first h of onset. After that, the thrombosis will be gradually absorbed and patients will experience less pain. As a result, surgical removal of acute thrombus or excisional hemorrhoidectomy may be offered if patients experience severe pain especially within the first 48 h of onset. Otherwise, conservative measure will be exercised including pain control, warm sitz baths, and avoidance of constipation or straining.
A resolving thrombosed external hemorrhoid could leave behind as a residual perianal skin tag -which may or may not require a subsequent excision. Hemorrhoids are very common during pregnancy especially in the third trimester[ 41 ]. Acute crisis such as profound bleeding and irreducible prolapsing may be found in pregnant women with pre-existing hemorrhoids. Since hemorrhoids and its symptoms will gradually resolve after giving birth, the primary goal of treatment is to relief acute symptoms related to hemorrhoids - mostly by means of dietary and lifestyle modification.
Kegel exercises, lying on left side, and avoidance of constipation could reduce the episode and severity of bleeding and prolapse. Fiber supplement, stool softener and mild laxatives are generally safe for pregnant women. Topical medication or oral phlebotonics may be used with special caution because the strong evidence of their safety and efficacy in pregnancy is lacking. In case of massive bleeding, anal packing could be a simple and useful maneuver. Hemorrhoidectomy is reserved in strangulated or extensively thrombosed hemorrhoids, and hemorrhoids with intractable bleeding.
In general any intervention or operation should be avoided, or performed with a careful consideration in immunocompromised patients because of an increases risk of anorectal sepsis and poor tissue healing in such cases[ 42 ]. A conservative measure is the mainstay for the treatment of hemorrhoids in this group of patients. If required, injection sclerotherapy appeared to be a better and safer alternative to banding and hemorrhoidectomy for treating bleeding hemorrhoids[ 43 , 44 ].
Antibiotic prophylaxis is always given before performing any intervention, even a minor office-based procedure, due to the possibility of bacteremia. A clinician must differentiate bleeding hemorrhoids form bleeding anorectal varices because the latter can be managed by suture ligation along the course of varices, transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt, or pharmacological treatment of portal hypertension[ 1 ].
Since a majority of bleeding hemorrhoids in such patients is not life threatening, conservative measure with the correction of any coagulopathy is a preferential initial approach. Of note, rubber band ligation is generally contraindicated in patients with advanced cirrhosis due to the risk of profound secondary bleeding following the procedure. Injection sclerotherapy is an effective and safe procedure for treating bleeding hemorrhoids in this situation. In a refractory case, suture ligation at the bleeder is advised.
Hemorrhoidectomy is indicated when bleeding hemorrhoids are refractory to other approaches. Anticoagulant or antiplatelet drugs may promote anorectal bleeding in patients with hemorrhoids and increase risk of bleeding after banding or surgery[ 45 ]. Unless the bleeding is persistent or profound, the discontinuity of antithrombotic drugs may be unnecessary because most of the bleeding episodes are self-limited and stop spontaneously.
Conservative measure is therefore the mainstay treatment in these patients. Injection sclerotherapy is a preferential treatment for bleeding low-graded hemorrhoids refractory to medical treatment. Rubber band ligation is not recommended in patients with the current use of anticoagulant or antiplatelet drugs due to the risk of secondary bleeding. If banding or any form of surgery for hemorrhoids is scheduled, the cessation of anticoagulant or antiplatelet drugs about d before and after the procedure is suggested[ 46 ].
To date, it is obvious that, apart from oral flavonoids-based phlebotonic drugs, currently available medication for hemorrhoids has no or limited beneficial effects on bleeding and prolapsing[ 19 ]. Since emerging evidence has suggested that perivascular inflammation, dysregulation of the vascular tone and vascular hyperplasia could play an important role in the development of hemorrhoids[ 2 ], the microcirculatory system of hemorrhoid tissue could be a potential and robust target for medical treatment.
The combinations of vasoconstrictive and venoconstrictive agents, with or without anti-inflammatory drugs, might be a new pharmacological approach for hemorrhoids. If an intervention, either office-based procedure or surgery - is indicated, evidence-based approaches must be exercised. Day-case operation or ambulatory surgery should be fully developed together with an effective program for peri-operative care[ 30 ]. Despite advances in office-based procedures and better surgical approaches, post-procedural pain and disease recurrence remain the most challenging problems in the treatment of hemorrhoids.
Consequently, future researches and novel management of hemorrhoids may focus on how to minimize pain following a procedure and how to prevent recurrent hemorrhoids. Meanwhile, long-term results of newly or recently developed interventions are definitely required.
- Dawns Dark Desire: Interracial Fantasies Volume One.
- These 7 natural remedies will help you cure hemorrhoids!
- Husbands How to Win Your Wifes Love and Respect;
In conclusion, the better understanding of the pathophysiology of hemorrhoids would prompt the development of effective treatments for hemorrhoids. Preventive measures, by means of dietary and lifestyle modification, may be the best treatment of hemorrhoids. Post-procedural pain and disease recurrence remain the most challenging problems in the treatment of hemorrhoids. The author declare no conflict of interest.