Have WAVELENGTH, Will Travel
Waves on a string or waves on the surface of water are examples of transverse waves. If we look at a graph of the air displacement versus position of the air, we can see that as the wave travels the shape of this wave travels to the right.
What are Electromagnetic and Mechanical waves?
So, the speed of a sound wave can be found by finding the speed of the peaks or the speed of the valleys or the speed of any single point on the wave shape. To figure out a formula for the velocity of a sound wave, let's look closely at what's happening here. Watch one of the air molecules. It takes one period for this molecule to move back and forth through a full cycle. During this time, the wave shape has moved forward one complete wavelength.
This is because the wave has to overlap with its initial shape after one period, because the molecule has to be back where it started after one period. Now, since speed is defined to be the distance per time, the speed of a sound wave has to be the wavelength of the wave divided by the period of the wave.
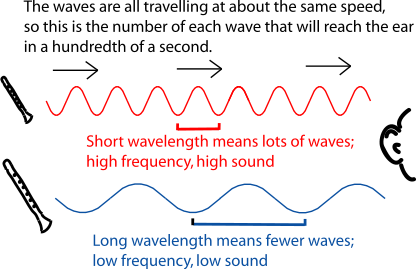
Since the wave is traveling forwards one wavelength per period, or since the frequency is defined to be one over the period, we can rewrite this formula as speed equals wavelength times frequency.
This formula is accurate for all kinds of waves, not just sound waves, because a wave has to move one wavelength for every period. When looking at this equation, you might think that if you adjust the setting on your speaker and increase the frequency you'd also be increasing the speed of the sound wave, but that's not what happens. If you increase the frequency, the wavelength will decrease by that same factor, and the speed of the sound wave will remain the same.
In fact, there's nothing you can do to the speaker that would increase the speed of sound. So, how can we change the speed of sound? Well, the only way to change the speed of sound is to change the medium or the properties of the medium that the sound wave is traveling in.
Sound and Light
So, to change the speed of sound in air, you can change things like the temperature of the air or the humidity of the air or the density of the air, or you can swap out the air entirely for another material, like water or helium or a metal. All of these changes to the medium would affect the speed of sound.
People often think that changing the amplitude will change the speed of a sound wave, but it won't. If we create a sound pulse with a large amplitude, it won't travel any faster than a sound pulse with a small amplitude in the same medium. Waves travel through tighter ropes at higher speeds. So while the frequency did not affect the speed of the wave, the tension in the medium the rope did. In fact, the speed of a wave is not dependent upon causally affected by properties of the wave itself.
Rather, the speed of the wave is dependent upon the properties of the medium such as the tension of the rope. One theme of this unit has been that "a wave is a disturbance moving through a medium. These media are distinguished by their properties - the material they are made of and the physical properties of that material such as the density, the temperature, the elasticity, etc. Such physical properties describe the material itself, not the wave.
On the other hand, waves are distinguished from each other by their properties - amplitude, wavelength, frequency, etc. These properties describe the wave, not the material through which the wave is moving. The lesson of the lab activity described above is that wave speed depends upon the medium through which the wave is moving. Only an alteration in the properties of the medium will cause a change in the speed.
A teacher attaches a slinky to the wall and begins introducing pulses with different amplitudes. Which of the two pulses A or B below will travel from the hand to the wall in the least amount of time? The amplitude of a wave does not affect the speed at which the wave travels. Both Wave A and Wave B travel at the same speed.
The speed of a wave is only altered by alterations in the properties of the medium through which it travels. The teacher then begins introducing pulses with a different wavelength. Which of the two pulses C or D will travel from the hand to the wall in the least amount of time? The wavelength of a wave does not affect the speed at which the wave travels. Both Wave C and Wave D travel at the same speed. Two waves are traveling through the same container of nitrogen gas.
Wave A has a wavelength of 1. Wave B has a wavelength of 4. The medium is the same for both of these waves "the same container of nitrogen gas". Thus, the speed of the wave will be the same. Alterations in a property of a wave such as wavelength will not affect the speed of the wave. Two different waves travel with the same speed when present in the same medium. An automatic focus camera is able to focus on objects by use of an ultrasonic sound wave. The camera sends out sound waves that reflect off distant objects and return to the camera. A sensor detects the time it takes for the waves to return and then determines the distance an object is from the camera.
The camera lens then focuses at that distance. Now that's a smart camera! In a subsequent life, you might have to be a camera; so try this problem for practice:. If it takes 0. While hiking through a canyon, Noah Formula lets out a scream. An echo reflection of the scream off a nearby canyon wall is heard 0.
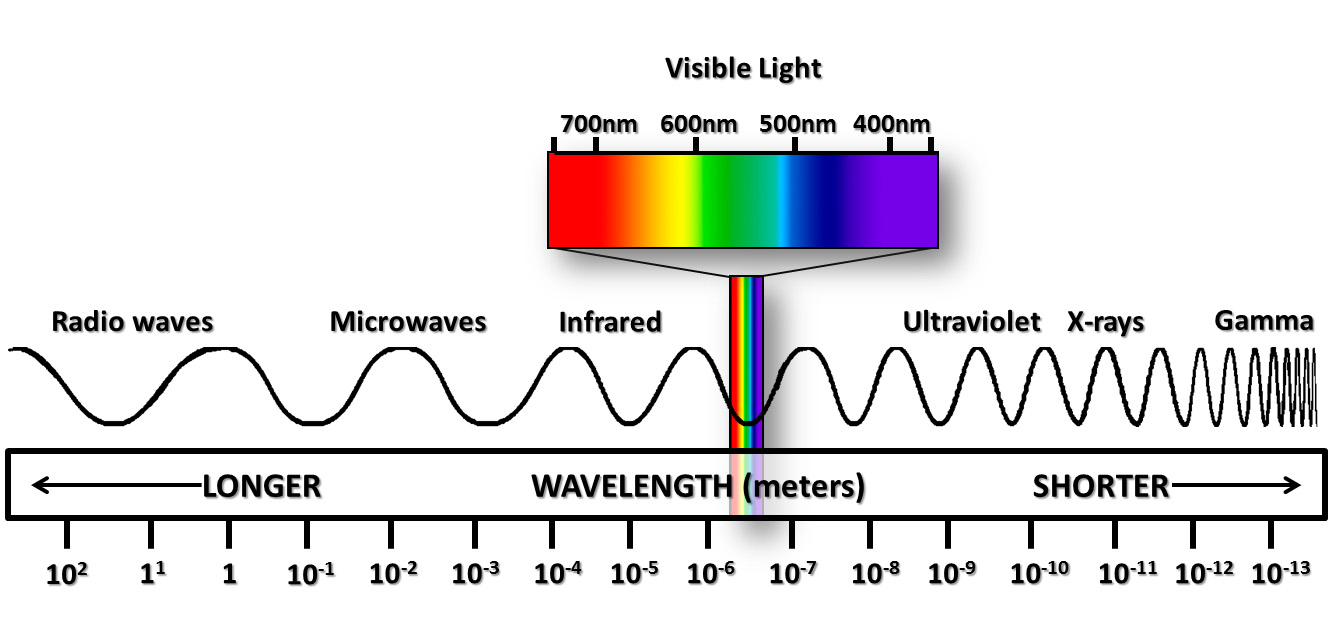
Electromagnetic Radiation
Calculate the distance from Noah to the nearby canyon wall. Mac and Tosh are resting on top of the water near the end of the pool when Mac creates a surface wave. The wave travels the length of the pool and back in 25 seconds. The pool is 25 meters long. Determine the speed of the wave. If the pool is 25 meters long, then the back-and-forth distance is 50 meters. The wave covers this distance in 25 seconds.
The water waves below are traveling along the surface of the ocean at a speed of 2. Each adjacent crest is 5 meters apart. The crests splash Wilbert's feet upon reaching his perch. How much time passes between each successive drenching? Answer and explain using complete sentences.
If Wilbert gets drenched every time the wave has traveled 5. Read Watch Interact Physics Tutorial.
What Can Teachers Do