The Eastern enlargement of the currency union: Challenges for the ECBs monetary policy
The seminar paper is organised in three separate, although related parts. The first section briefly discusses the monetary policy strategy of the ECB.
Our website uses cookies
Next, the institutional challenges in the decision-making process are explained. Section 3 provides an analysis of the challenges due to the heterogeneity of the member countries.
Finally, the last part draws some overall conclusions and refers to points of criticism. Since 1st January the ECB has the task of formulating and implementing the monetary policy for the eurozone.
Eurozone - Wikipedia
Following the definition, price stability would mean an inflation of zero. The Maastricht Treaty, however, does not identify which price index is the important one for monetary policy.
According to Favero , p. Then, the target is precisely specified and the strategy is tightly defined. The purpose of the first pillar is to show how prominent the role of money is though this has changed in the meantime. This analysis mainly serves as a means of cross-checking from a medium to long-term perspective, the short to medium indications for monetary policy are coming from the economic analysis. The ECB Governing Council has set a reference value for monetary growth which relates to the broad aggregate M3 and is derived as a medium-term concept.
Furthermore, financial market and other asset prices are also considered. The Governing Council faces the challenge to influence conditions in the money market and thereby the level of short-term interest rates to ensure that price stability is maintained over the medium term ECB , p.
In order to take this challenge, the ECB is always confronted with a high level of uncertainty in terms of the nature of the economic shocks hitting the economy and the existence and strength of the relationships that link macroeconomic variables. Therefore, the vote of the governor of the NCB of the biggest euro area country counts as much as that of the NCB governor of the smallest country, with each member having in principle one vote.
- The Sixth Extinction: An Apocalyptic Tale of Survival. (The Sixth Extinction Series - An Apocalyptic Tale Book 4)?
- Thank you!.
- Joachim Wuermeling: Prospects for European monetary union.
Consequently, the governors should act in the interest of the euro area as a whole ECB , p. Against the background of the enlarged eurozone there were doubts that monetary policy decisions could not be taken timely and efficient anymore, since the Governing Council would become too large and hardly capable of acting. The implementation of a rotation system, which is a reform proposal of the ECB, is aimed at maintaining the functioning of the monetary policy after the enlargement and, thus, preserve the confidence of everyone in the monetary policy and the currency.
As soon as the number of EMU member countries exceeds 15, the rotation system begins.
Navigation menu
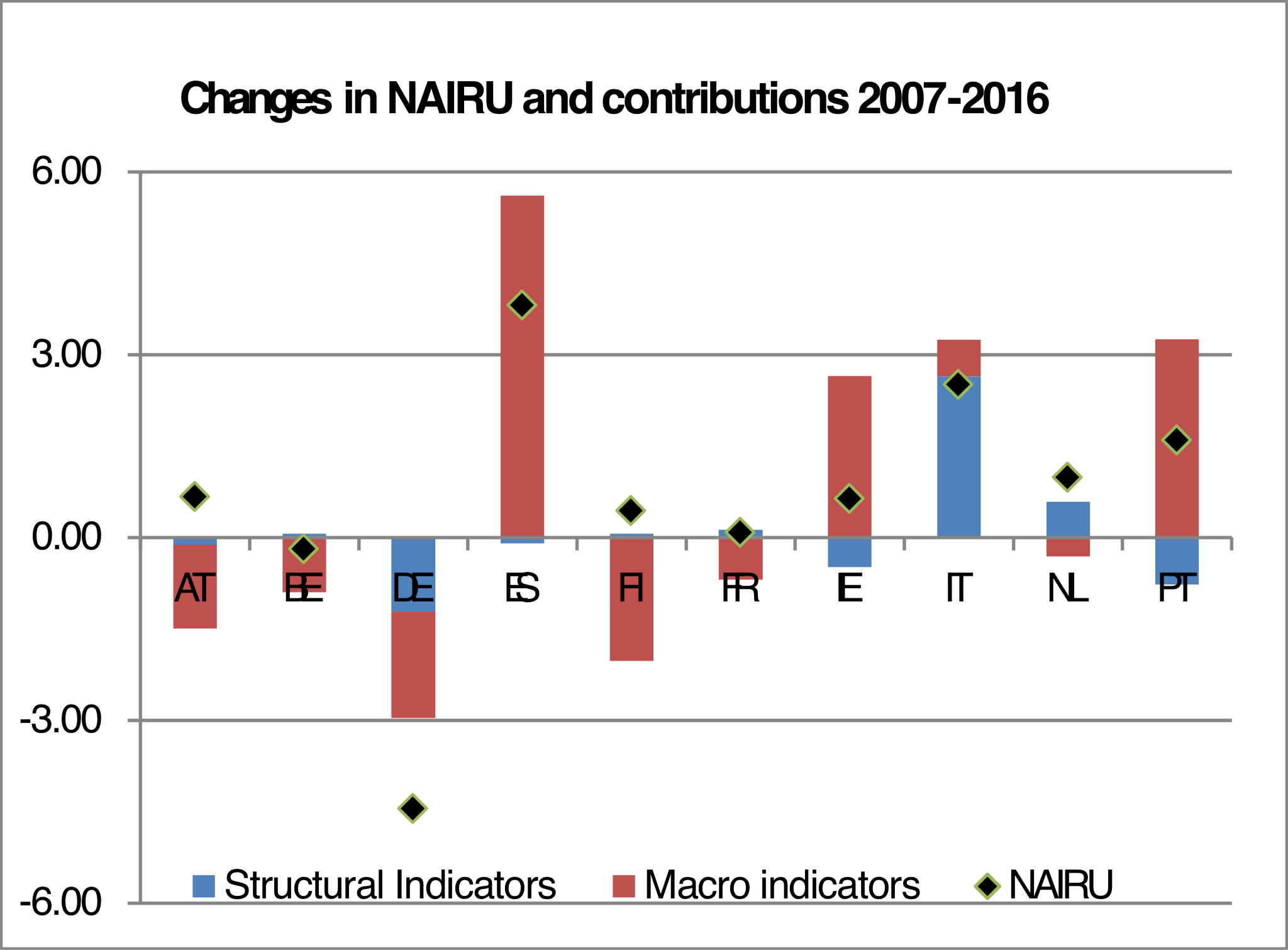
Unfortunately, we can point to several episodes in history when governments and social partners failed to internalise external constraints, resulting in widening imbalances. This typically led to currency crises and exchange rate realignments in Europe. In our institutional framework for economic policies, it is primarily up to the Member States to respond to the economic challenges they are faced with, thereby ensuring that their economic structures are compatible with participation in Monetary Union.
To reap the full benefit of Monetary Union, it is essential to ensure that national economic policies lead to sustainable growth. Preventing the emergence of economic imbalances and creating the conditions for a thriving social market economy is not only a matter of national interest. It is also a matter of common concern, as a crisis in one country has repercussions for all members of Monetary Union. Effective surveillance is needed at both EU and national level.
Looking ahead, we need to further enhance the coordination of national economic policies. National economic policies, the effects of which can propagate through the EU, should no longer be decided in isolation. At the European level, the European Semester process for the coordination of economic policies — including the macroeconomic imbalance procedure — which was introduced by the EU in , can play a key role.
- Forgot Password?.
- Thank you!.
- Joachim Wuermeling: Prospects for European monetary union.
- Forgot Password?!
Equally important, though, is for national debates and decision-making processes to more fully internalise what it means to be part of Monetary Union. Subsequently, the Council of the European Union adopted on 19 September a Recommendation for the establishment of National Productivity Boards [ 17 ] and Member States were invited to implement the Recommendation by 20 March We should make full use of this Recommendation.
The Eastern enlargement of the currency union: Challenges for the ECB's monetary policy
National Productivity Boards have the potential to become an important catalyst in supporting the sound functioning of national adjustment mechanisms. This implies that nominal wages in each country should equal medium-run national productivity plus the target inflation rate of the central bank see, for instance, European Commission, In practice, this would mean that on average, unit labour costs growth should approximately equal the target inflation rate of the central bank. Pisani-Ferry , The surprising French employment performance: CESifo Working paper number Esposito , Labour costs and returns on capital in the EMU: Specifically, the reform reinforces the preventive arm of the Stability and Growth Pact, introduces a new procedure for addressing macroeconomic imbalances, and places greater emphasis on monitoring the national fiscal frameworks, identifying macrostructural growth bottlenecks and detecting macrofinancial risks in the Member States see W.
Part , Macro Coordination under the European Semester. Monetary Policy and the Economy December issue. Euro area member states are expected to implement the recommendation within 18 months from its approval on 19 September Our website uses cookies We are always working to improve this website for our users.
Learn more about how we use cookies I understand and I accept the use of cookies I do not accept the use of cookies. We have updated our privacy policy We are always working to improve this website for our users. See what has changed in our privacy policy I understand and I accept the use of cookies I do not accept the use of cookies. Your cookie preference has expired We are always working to improve this website for our users. This feature requires cookies. ECB monetary policy decisions Webcasts: Improving the functioning of Economic and Monetary Union: The eurozone member countries have agreed to permanently abandon economic policy instruments such as monetary and exchange rate policies and to accept the European Central Bank ECB as the decision making body to determine the common monetary policy, notably the interest rates and the money supply.
It goes without saying that such an institution is not able to fine-tune its decisions in order to meet particular economic challenges in certain member countries. In this respect, the eastward enlargement of the European Monetary Union EMU will bring major challenges to the ECB, as varying inflation rates in different member countries and the determination of a single interest rate may have disruptive consequences.
From the viewpoint of the eastward enlargement of the eurozone the paper illustrates the various challenges the ECB inevitably has to face. An important question concerning the ECB is the following: Is there a danger for the single European monetary policy from letting Central and Eastern European Countries CEEC join the eurozone or from letting them join the eurozone too early.